RPCEmu Networking Guide
Introduction
RPCEmu supports the use of Networking in RISC OS.
There are 3 different methods of networking that RPCEmu supports.
You are highly recommended to use the following method.
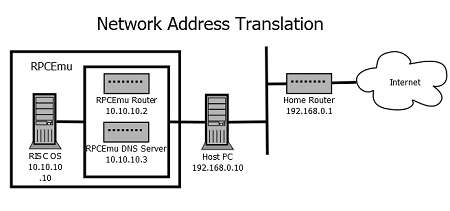
- Network Address Translation - Works by creating a virtual network and virtual 'router' inside the RPCEmu binary. Supported by both Windows and Linux. It is the easiest method to configure.
Alternativly configuring these two types of networking are fairly involved and more complex than configuring other aspects of RPCEmu..
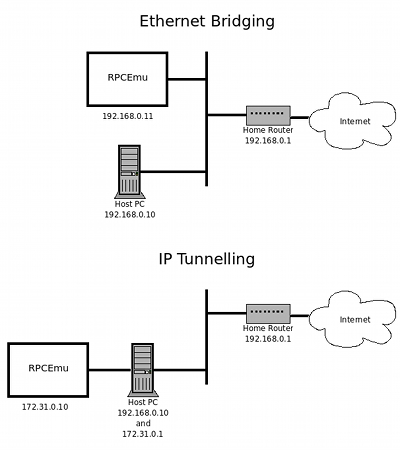
- Ethernet Bridging - Works by effectively placing an additional network interface visible on your home network. Supports all protocols that can be transmitted over Ethernet, including IP.
- IP Tunnelling - Only available on Linux. Creates an additional IP Network to run between your Host Operating System and the emulator. Requires you to setup IP routing on your Host Operating System and only supports IP based protocols.
- Basic TCP/IP networking knowledge.
- The IPv4 addresses and netmask of your network's gateway and DNS server.
- A spare static IP address on your network (if Ethernet Bridging).
You will need these prerequisites before you start to configure Ethernet Bridging or IP Tunnelling.
Here are network overviews of how each type of networking appears to other machines on the network, using the example of a simple home network.
FOLLOW ONLY ONE METHOD'S INSTRUCTIONS
Windows/Linux Network Address Translation (Reommended) Windows Ethernet Bridging Linux IP Tunnelling- Linux binary configuration
- Linux configuration (IP Tunnelling)
- RISC OS Install Network Boot
- RISC OS Configuration - IP Tunnelling
Contributors: Peter Howkins, Dick Tanis, Tom Hughes